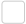
Approaches to multiple sclerosis therapy
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common autoimmune disease of the central nervous system and one of the most common non-traumatic disabling diseases to affect young adults. There is currently no single defined cause for the development of MS, though those diagnosed are likely to have a genetic predisposition to the condition.
Here we outline the two approaches to MS therapy:
Disease modifying treatments – reduce MS relapses and slow down the damage caused over time
Development of
multiple sclerosis
Treatment to reduce MS relapse
80-85% of people with multiple sclerosis experience a relapse1.
Treatment with beta interferon or glatiramer acetate can help prevent relapse
Immune reconstitution therapies
Aim to reset the immune response caused in MS.
Ocrelizumab targets CD20 on B cells.
Alemtuzumab targets CD52 on T and B cells.
Neurodegeneration therapies
Target the autoimmune response which causes neurodegeneration.
Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors mediate B cell function – in phase 1 and 2 clinical studies
Treatments for the consequences of MS – target the degenerative effects of the disease
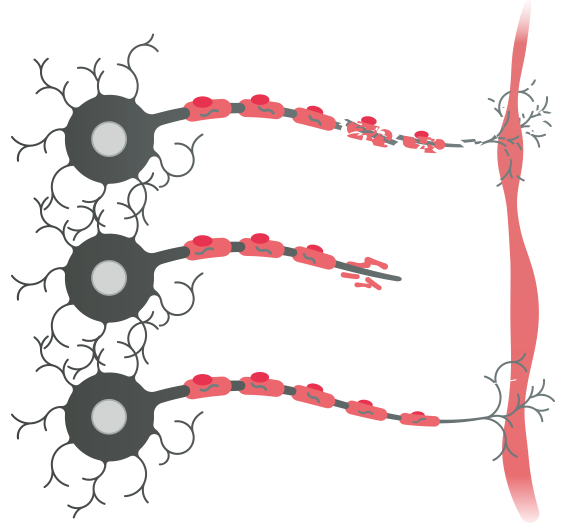
Remyelination therapies
Aim to replenish myelin lost as a result of MS.
Opicinumab, a LINGO-1 inhibitor – in phase 3A clinical trials
High-dose biotin stimulates myelination – in phase 3 trials
Neuroprotection therapies
Protect against nerve cell damage and loss.
Sodium channel blockers and phenytoin (an anticonvulsant) have been shown to reduce nerve cell loss by 30% in clinical trials2
Neurorestoration therapies
Restore the nerve damage caused by MS.
Repulsive guidance molecule A (RGMA) monoclonal antibody encourages axonal sprouting – in phase 2 trials
Slowing aging mechanisms
Combat the symptoms of accelerated aging associated with MS.
High dose simvastatin reduces cholesterol and reduces brain volume loss
Exercise and good diet
Find out more at
www.abcam.com/MS
References
1) De Angelis et al, (2018) BMJ
2) Raftopoulos et al, (2016) Lancet Neurol
Download the PDF
Abcam will process your personal data in strict accordance with its privacy policy which can be found here. This will include sending you updates about Abcam, our products, and resources we think would be of interest to you. You can unsubscribe and manage your marketing preferences by clicking the link at the bottom of every email we send. By filling out this form you consent to Abcam sharing your details with your local, authorized distributor for the purpose of answering your query.